Image Based Modeling, Measurement and Analysis
VOXELCON
Analysis
Using voxel model created from CT-images or STL model, you can execute stress analysis, steady-state heat conduction analysis, and homogenization analysis etc.
Static Stress Analysis
You can analyze a complicated model easily without troublesome mesh generating. Boundary conditions can be set not only to voxel model but to STL model.
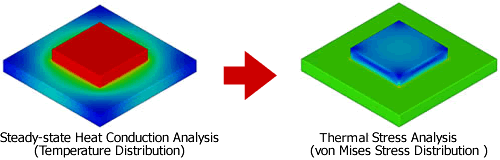
Steady-state heat conduction analysis/ Thermal stress analysis coupled with heat conduction analysis.
You can excute "steady-state heat conduction analysis", and "Coupled thermal stress analysis".
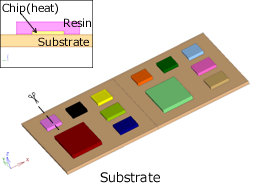
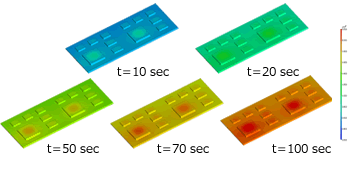
Unsteady Heat Conduction Analysis
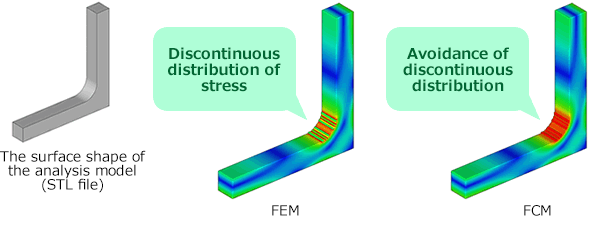
Analysis Using the Finite Cover Method (FCM)
The Finite Cover Method (FCM) is used to perform static analysis and steady-state heat conduction analysis.
VOXELCON can read STL files, apply boundary conditions to their surface geometry, and perform analysis. When applying boundary conditions to STL files, there are two methods: the finite element method, which approximates the boundary conditions of the voxel mesh to the voxels based on their spatial relationship; and the finite cover method, which recognizes the STL geometry intersecting the voxels and approximates the local region more precisely.
For shapes with R-parts, the voxel-specific model shape representation tends to cause a ‘discontinuous distribution of stress’ where high and low stress distribution alternate on step edges. The finite covering method avoids this phenomenon, enabling detailed stress evaluation.
Multi-Scale Analysis by the Homogenization Method
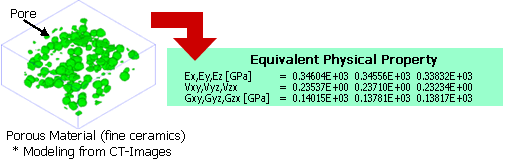
Based on the theory of homogenization method, VOXELCON can deal with the material which has a detailed micro structure compared to whole structure. ( e.g. Composite Material and Porous Material )
Equivalent Physical Property
Based on the homogenization method, it can calculate equivalent physical-property values of composite materials or porous materials etc. The calculable physical-property values are as follows.
- Equivalent Elastic Coefficient
- Young's Modulus, Poisson's Ratio, Shearing Modulus - Equivalent Linear Expansion Coefficient
- Equivalent Thermal Conductivity
- Equivalent Permeability Coefficient
Localization
After analyzing macro structure (the whole structure) using the calculated equivalent physical property, you can evaluate stress distribution of any point. It's called "Localization".
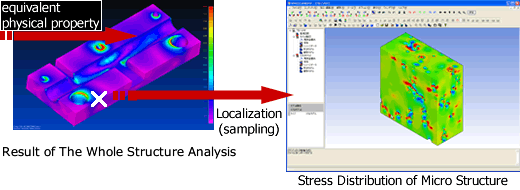
* Japan Fineceramics Center
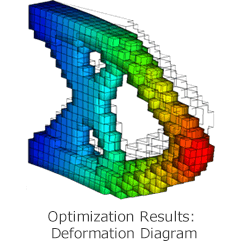
Topology Optimization
It features topology optimization using the level set method.
The stiffness maximization subject to the volume constraint is available.
VOXELCON enables easy structural optimization and outputs a smoothed STL file along with structural analysis results such as displacement.

Others
Matrix Solver / Parallel Performance
Matrix solver adopts the parallelized PCG solver using "Element by Element Method", which is specialized to voxel analysis. You can analyze a large-scale model with saving memory.
(Standard : up to 2 threads , Option : more than 2 threads)
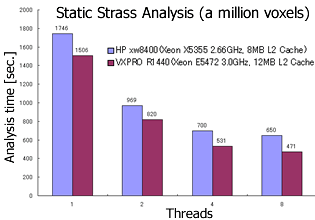
* Tokyo Dental College Anatomy Dep. Dr. Yoshinobu Ide, Scalable Systems Co., Ltd.
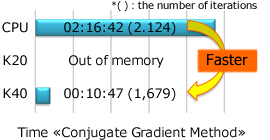
Massively parallel solver for GPU
* Option
* Collaboration : Gifu University Dr. Eng. Gakuji Nagai
Analysis Performance
Static Stress Analysis : Aluminum Foam
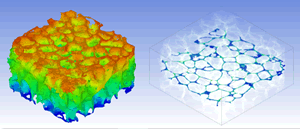
| Number of Voxels | 42,960,471 |
|---|---|
| Number of Materials | 1 |
| Porosity | 16.4% |
| Data | CT Images |
| Analysis Condition | Constraint, Enforced Displacement |

Large Scale Model Analysis
 It is possible to analyze also 100 million or more voxels by VOXELCON.
It is possible to analyze also 100 million or more voxels by VOXELCON.
In recent years, PC with tens of memory can be obtained easily.
If such machine resources are utilized, You can tackle large-scale analysis like 100 million voxels with PC.
The memory usage of 100 million voxels
-> about 25 GB (Static Stress Analysis)
* Tokyo Dental College Anatomy Dep. Dr. Yoshinobu Ide
Output Data - Nastran,I-DEAS,ANSYS
Voxel models and boundary conditions which are created in VOXELCON can be converted to Nastran Bulk Data, I-DEAS Universal Data and ANSYS CDB data.
Various Post Processing
Defomation / Showing Contour
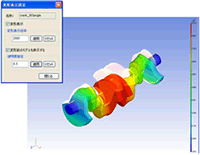
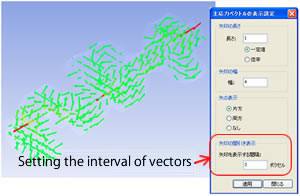
Principal Stress Vectors
Stress on the measurement line / Histogram
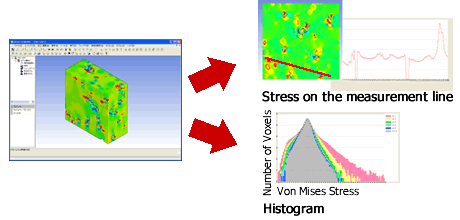
* Japan Fine Ceramics Center